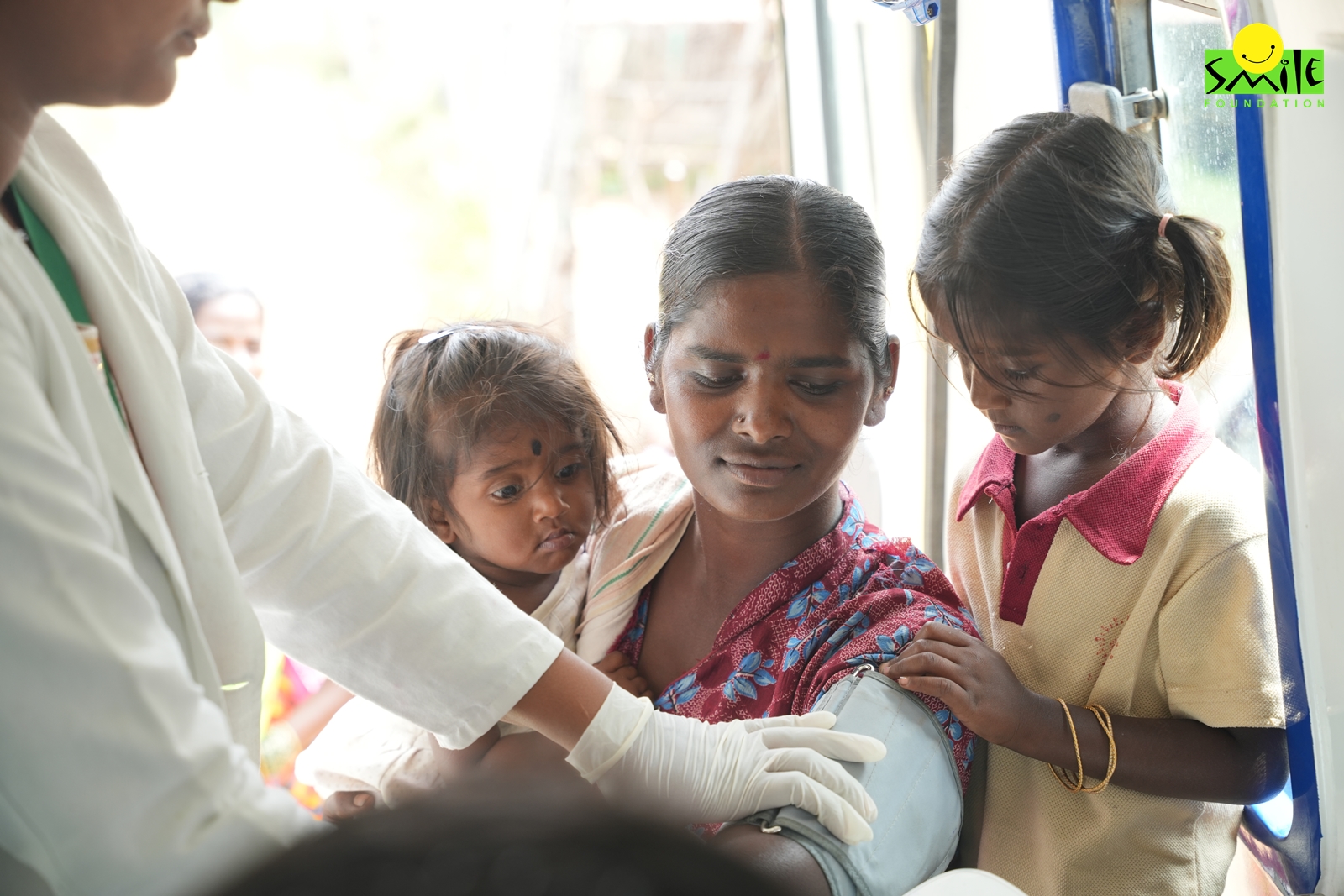
While healthcare services have improved over the years, rural women continue to face significant barriers to accessing modern medical care. Factors like financial constraints, lack of awareness, social taboos, and limited availability of healthcare facilities make the situation challenging.
Traditional medicine, which has been practiced in India for centuries, still holds a strong presence in rural areas. Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani have been used for generations and are often the first line of treatment. While modern healthcare provides scientifically validated treatment, traditional medicine offers a more holistic approach that aligns with cultural beliefs and local practices. Striking a balance between these two systems can be key to improving rural women’s health outcomes.
The Current State of Women’s Health in Rural India
Women in rural India suffer from multiple health issues, ranging from malnutrition and anemia to pregnancy-related complications and chronic diseases. According to the National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5), over 57% of women aged 15-49 in rural areas are anemic. Maternal mortality remains a significant concern, with India recording a maternal mortality ratio (MMR) of 97 per 100,000 live births in 2018-2020, with rural areas contributing disproportionately to this figure. Additionally, non-communicable diseases (NCDs) like hypertension and diabetes are increasing, affecting women’s long-term health. Access to quality healthcare is hindered by poor infrastructure, lack of transportation, and deeply rooted gender discrimination that often places women’s health needs at a lower priority than those of men.
Women often face neglect when it comes to receiving medical care, as family resources are typically allocated to men first. Report suggests that women in rural households are less likely than men to seek healthcare when sick. Social norms and lack of transportation discourage women from traveling alone to healthcare facilities, and many rely on male family members. Traditional medicine, often practiced within communities by women themselves, offers an alternative where women feel more comfortable and empowered to seek care, thereby improving their health-seeking behaviour.
Where Modern Healthcare Falls Short
Despite its advancements, modern healthcare is not easily accessible to rural women. Rural areas often lack well-equipped hospitals or even basic primary healthcare centers. A 2019 report stated that 75% of India’s healthcare infrastructure is concentrated in urban areas, leaving rural populations underserved. Even with government schemes like Ayushman Bharat, out-of-pocket healthcare expenses remain high, discouraging women from seeking medical attention. Cultural and social barriers also play a significant role, as gender norms often prevent women from visiting male doctors or prioritizing their health over family responsibilities.
In many villages, women hesitate to discuss reproductive or menstrual health concerns, leading to undiagnosed and untreated conditions. Moreover, some rural communities have a deep-rooted mistrust of modern medicine, viewing it as foreign or unnatural compared to traditional practices they have relied upon for generations. Telemedicine, however, is emerging as a potential solution to bridge this gap. The expansion of digital health services and mobile healthcare units has shown promise in overcoming geographical barriers, allowing women to consult healthcare providers remotely without the need to travel long distances.
The Role of Traditional Medicine in Bridging the Gap
Traditional medicine has been an integral part of India’s healthcare system for centuries. Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani treatments are widely practiced, and herbal remedies are commonly used in rural households. Several studies have shown the effectiveness of traditional medicine in addressing specific health concerns.
Traditional medicine provides diverse remedies and therapies to support women’s reproductive health across various life stages, offering affordable and accessible solutions to those who might otherwise go untreated. For instance, ayurvedic formulations like Ashwagandha and Shatavari can enhance reproductive health and manage pregnancy-related complications. Traditional herbal treatments can help address menstrual irregularities, fertility concerns, and postpartum care, promote healing and recovery.
Chronic disease management through traditional practices such as yoga and naturopathy has also proven effective in managing hypertension, diabetes, and arthritis. Studies have indicated that a combination of Ayurveda and modern interventions can significantly improve health outcomes.
Where’s India at?
Recognizing the potential of traditional medicine, the Indian government has actively promoted its integration with modern healthcare. The Ministry of AYUSH (Ayurveda, Yoga & Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy) was established to regulate and promote traditional healing practices. Governments are making provisions to recruit AYUSH doctors in primary healthcare centres to integrate traditional medicine with modern medical services. The National AYUSH Mission aims to strengthen AYUSH services in rural areas by establishing dedicated healthcare centers.
Several states have also trained ASHA workers to incorporate traditional medicine into their services, providing accessible and culturally acceptable healthcare to rural women. By integrating AYUSH practitioners with modern medical professionals, India is working towards a more comprehensive healthcare system that caters to the diverse needs of its rural population.
The Way Forward
Looking at the current state of women’s health in rural areas, India must adopt a healthcare model that seamlessly integrates modern and traditional medicine to enhance health holistically. Expanding access through telemedicine and mobile health services can ensure timely care, while education and awareness campaigns will help women make informed choices about their health. Traditional practices should be scientifically validated, with research refining and standardizing herbal treatments for broader acceptance. Encouraging AYUSH practitioners to collaborate with modern doctors can bridge the gap between tradition and science, creating a comprehensive system that serves rural women effectively.
Rather than debating which system is superior, India should focus on merging their strengths. Modern healthcare provides scientific rigor and life-saving interventions, while traditional medicine offers culturally familiar, community-driven solutions. A blended approach will empower rural women, respecting their beliefs while ensuring they receive the best possible care. With the right policies and infrastructure, India can build a healthcare framework where rural women no longer have to choose between tradition and modernity.
Smile Foundation has been actively addressing the health needs of rural women. Recognizing the challenges these women face—such as limited access to modern healthcare, financial constraints, and cultural barriers—the Foundation supports initiatives that bridge this gap. Through their community-based programs, Smile Foundation works to raise awareness about women’s health and provides access to modern medical services. In doing so, Smile Foundation ensures that rural women have access to comprehensive healthcare improving overall health outcomes.