That unemployment is a major concern for any country, including India, is not a matter of question. However, understanding how unemployment manifests itself can go a long way in dealing with the problem and coming up with effective solutions. India is a big country with more than 1.4 billion people. A vast majority of this population is employable because the country is the youngest in the world. However, a massive unorganised labour market has two distinct threads that stand out: disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment. It is crucial for policymakers to understand these nuances to craft necessary solutions that may help in reducing unemployment.
Let’s look at these in detail.
Disguised Unemployment
Disguised unemployment exists when part of the labour force is either left without work or is working in a redundant manner, resulting in essentially zero worker productivity. To understand this, let us look at an example. Let’s say that workers are required in a biscuit manufacturing unit. To support the demand, there’s a need for 100 workers who can effectively complete the work on time. However, the employer hires 150 workers for the same job. What will happen now?
Either the extra 50 people will have no work to do, or less work will be allocated to all the workers to adjust for this surplus labour. So, disguised unemployment does not affect aggregate economic output. However, it also does not increase productivity. Thereby, leading to waste of human resources. Developing countries with big populations usually have to deal with this problem of disguised unemployment because their workforce keeps expanding while the job opportunities do not grow in tandem with it.
One way of dealing with this problem is to encourage the individuals to acquire diverse skills so that they can contribute to other tasks. It may also help in creating new opportunities for the workers. At the same time, policymakers should focus on promoting entrepreneurship, especially small businesses as they have the potential to create jobs for a large population.
Seasonal Unemployment
It is when jobs are available only during a specific time period in a year. Let’s say you work as a paragliding pilot in the Himalayas. Now, it is highly likely that you will only have work available to you during some months in the entire year when the weather conditions are favourable for flights. This means that for the rest of the year you will either have no work or have to find something else to do which may not be your core skill. This problem of seasonal unemployment is found in a number of industries and sectors which gives rise to uncertainty among the workers and creates dependency on making a year’s worth of wages in a short time. Therefore, many communities engaged in such seasonal employment sometimes have to struggle when the incomes are not as per expectations during the work season.
Again, what can help in this situation is diversification of skills and creating new work opportunities for the people. If there are options beyond what is available to them, people can engage themselves in other work when they are available. Also, entrepreneurship serves as a major solution to this problem as well. For example, the paragliding pilot may decide to open a small business like running a homestay or an eatery to make up for the lack of employment during some months in the year.
India’s Challenge
Despite overall improvements in labour force participation and employment rates, employment conditions in India remain poor. India’s youth account for almost 83% of the unemployed workforce. The share of educated youth (with secondary or higher education) in the total unemployed has almost doubled from 35.2% in 2000 to 65.7% in 2022. Disguised unemployment often manifests as stagnant or declining wages, increased self-employment among women, and a higher proportion of unpaid family work among youth.
According to the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE), the unemployment rate in India stood at 9.2% in June 2024. Seasonal unemployment is tied to cyclical industries such as agriculture, tourism, and retail. During peak seasons, jobs are available, but they vanish during off-seasons.
Both disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment are complex problems to deal with. Also, because these problems are highly localised and work-specific, it is important for policymakers to take a nuanced approach when creating solutions. In the end, workers’ benefits should be kept in mind. By weaving policies that address both, we can create a stronger, more resilient fabric for India’s workforce.
Smile Foundation and Employment of Youth
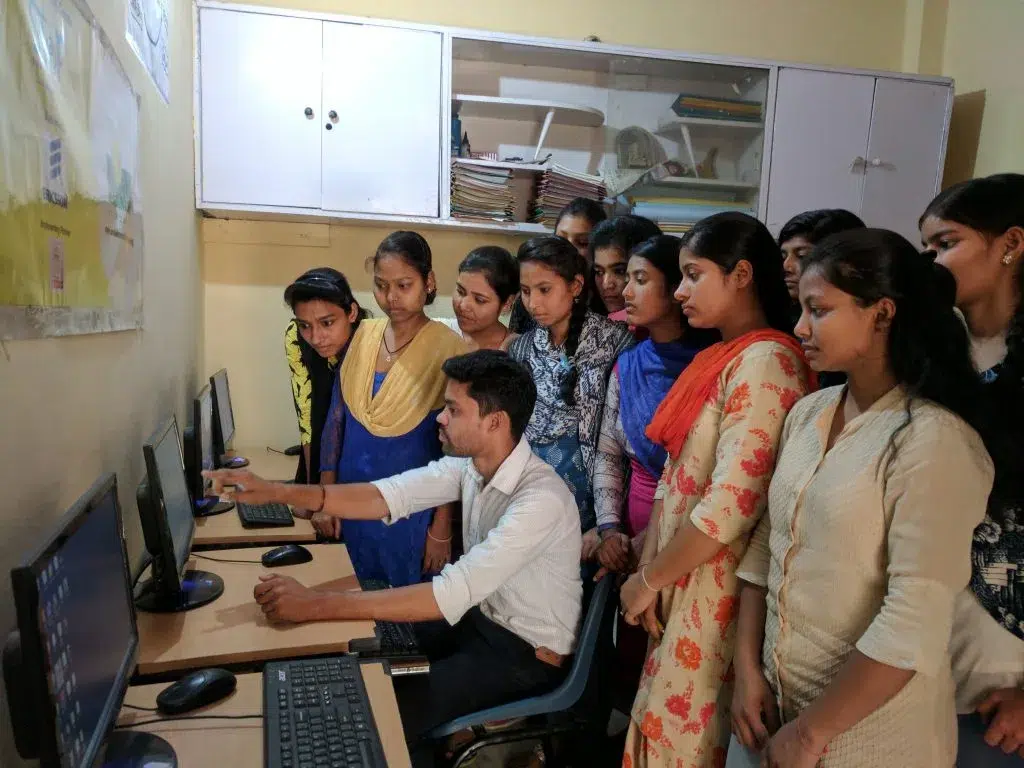
Smile Foundation has partnered with Amazon to establish 21st-century learning labs, equipping skilling centers with digital devices to enhance their capabilities. By collaborating with industry experts in skill development and vocational training, such as NIIT Foundation, Wadhwani Foundation, and Tata Strive, Smile Foundation has effectively implemented curriculums in core employability skills, BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance), GDA (General Duty Assistant), and Digital Marketing. These partnerships ensure our training programs align with industry standards, providing students with the essential skills needed for employment. Additionally, we have focused on building strong relationships with employers to facilitate job placements for our trained candidates. Our alliances with companies like Team Lease, Quess Corp, and Better Place support the successful placement of skilled youth into the workforce.