India, ranked as the fifth-largest economy of the world, is projected to ascend to the position of the third-largest economy by 2027, with a GDP surpassing US$ 5 trillion, according to IMF estimates. How does the Indian youth come into this equation?
Recently, the Prime Minister of India launched Viksit Bharat@2047: Voice of Youth. This initiative aims to turn India into a developed nation by 2047, marking the country’s 100th year of independence. It focuses on various aspects of development, including economic growth, social progress, environmental sustainability, and good governance. The government aims to involve every youth in the country in the plan for a developed India.
Notably, half of India’s GDP contribution is from its youth population, as it targets to become a US$ 30 trillion economy by 2047, embodying the traits of a developed nation.
Viksit Bharat@2047 and India’s youth potential
Data from the United Nations reveals that Indian youth population, aged between 15 and 34, surpasses 422 million, making up nearly one-third of the its total population. Additionally, the International Labour Organization highlights that youth employment plays a significant role in our overall employment landscape, particularly in sectors like agriculture, manufacturing, and services, where young workers are crucial for operational activities.
Realizing the large number of young people in the country, the state and other stakeholders understands that skill development is not just about finding jobs- it is about creating opportunities and potential for the Indian youth. By giving them the skills they need to succeed, the government is not just securing their financial well-being but nurturing a generation of innovators, entrepreneurs, and leaders who can shape the future of the nation.
Some good news!
According to the World Bank, Indian youth labor force participation rate increased from 48.9% in 2010 to 51.5% in 2020, indicating a growing presence of young workers in the economy.
In recent years, there has been significant growth in social and economic infrastructure, driven by policies and initiatives such as Samagra Shiksha and the expansion of universities, IITs, IIMs, and medical and nursing colleges, along with skill development programs like the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana. Over the past decade, the number of universities and colleges has multiplied, with the Indian higher education system now comprising 1,113 universities/university-level institutions, 43,796 colleges, and 11,296 standalone institutions, catering to 4.33 crore students. The Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) in higher education has also risen steadily to 28.4.
The young of India, with its creativity and potential for innovation, supported by government initiatives such as Digital India and Startup India, is increasingly becoming a force in job creation. The country now boasts over 100 unicorns, valued at over US$ 340 billion in total, and has established itself as the world’s third-largest startup ecosystem.
Skilling is an inclusive initiative
Skilling initiatives are increasingly recognized as powerful tools for economic growth and social inclusion. However, true inclusivity requires deliberate efforts to ensure that marginalized groups, including women, persons with disabilities (PWDs), and underserved communities, have equal access to skill development opportunities. By focusing on these groups, skilling initiatives can address systemic barriers and empower individuals to participate meaningfully in the workforce.
For women, inclusive skilling initiatives should prioritize tailored training programs that address their unique needs and challenges. Flexible scheduling, childcare support, and mentorship opportunities can help overcome barriers related to caregiving responsibilities and societal norms. Additionally, providing financial assistance and promoting entrepreneurship can empower women to become active contributors to India’s economy.
Similarly, PWDs face significant barriers to accessing education and employment opportunities. Inclusive skilling initiatives should offer accessible training facilities, adaptive technologies, and specialized support services to accommodate diverse abilities. By promoting disability-inclusive policies and a supportive environment, these initiatives can empower PWDs to develop valuable skills and pursue fulfilling careers.
Underserved communities, including rural populations, tribal groups, and migrant workers, often lack access to quality education and training. Initiatives should prioritize outreach efforts, mobile training units, and community-based programs to reach these marginalized groups.
Skill development initiatives for the Indian youth
Skill development policies in India have been formulated to address the challenges of unemployment, underemployment, and skill shortages, while also promoting economic growth and social inclusion.
National Skill Development Policy (2009): It was launched to create a skilled workforce capable of meeting the demands of a growing economy. It emphasizes the importance of vocational education and training (VET) to enhance employability.
National Skill Development Mission (2015): It focuses on scaling up skill training efforts, promoting entrepreneurship, and ensuring industry participation in skill development programs.
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): It offers short-term skill development courses aligned with industry standards and provides monetary rewards to trainees upon successful completion of training.
Skill India Mission: It’s a multi-skill development initiative launched to create a skilled workforce for various sectors, including manufacturing, construction, healthcare, tourism, and information technology.
Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (APS): The Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme aims to increase the engagement of industries in apprenticeship training and create opportunities for hands-on learning and skill development.
National Apprenticeship Training Scheme (NATS): NATS facilitates apprenticeship training for engineering and non-engineering graduates and diploma holders. It aims to bridge the gap between industry requirements and academic curricula by providing practical training in industries.
Skill Loan Scheme: It provides financial assistance to individuals seeking skill development training from recognized training providers. It offers low-interest loans to cover the cost of training fees, enabling individuals to acquire new skills and improve their employability.
Skilling the Indian youth: A collaborative approach
Skilling in India is undergoing a transformative shift towards a collaborative approach, leveraging the expertise and resources of various stakeholders to address the nation’s diverse skill development needs. Government initiatives like the Skill India Mission and the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) provide the overarching framework, while industry partnerships offer crucial insights into emerging skill demands and provide practical training opportunities. Educational institutions contribute by imparting foundational and specialized skills, while civil society organizations play an important role in addressing specific skill gaps and social barriers, particularly for marginalized groups. International partnerships facilitate knowledge exchange and capacity building, enriching Indian skilling ecosystem with global best practices.
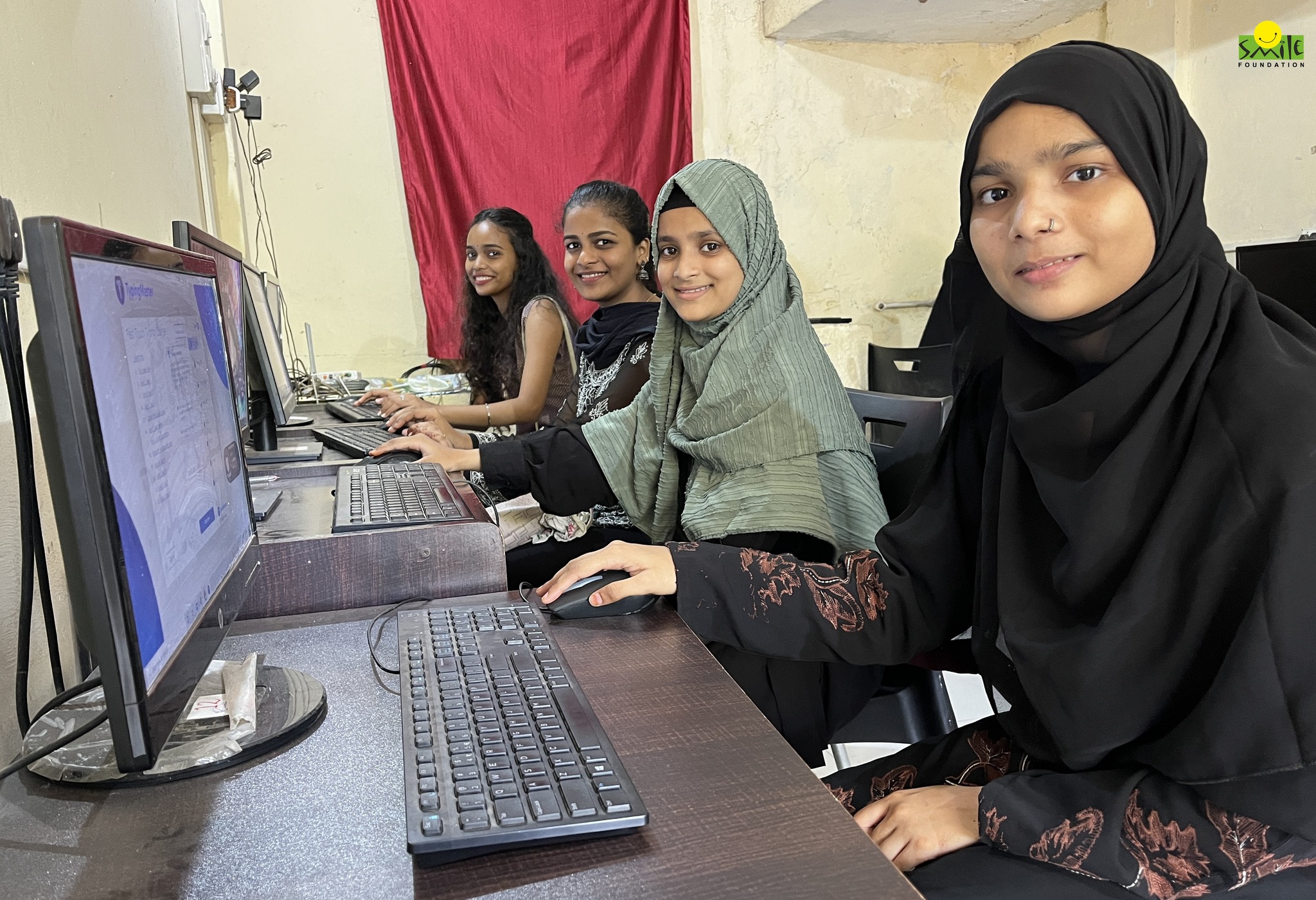
Our Smile Twin e-Learning Program (STeP) is a comprehensive initiative aimed at empowering underserved youth with employable skills, enabling them to secure sustainable livelihoods and break the cycle of exclusion. STeP focuses on providing vocational training, soft skills development, and placement assistance to marginalized youth, particularly from urban slums and rural areas. Through its holistic approach to skill development and livelihood promotion, Smile Foundation is empowering lacs of individuals, strengthening communities, and contributing to socio-economic development.