Quality healthcare access in rural India has always remained a challenge as rural areas are often disadvantaged due to their geographical isolation, shortage of medical professionals, and lack of improved infrastructure. Improved access to quality healthcare for rural populations is a pressing issue, with disparities in health outcomes and service availability compared to urban areas. These limitations often give rise to substantial delays in prompt care; people in rural areas are at greater risk of suffering premature death from heart disease, cancer, respiratory illnesses, and stroke.
Rural populations also tend to have a higher proportion of older adults, pregnant mothers, and newborns, who may require more frequent medical services, further exacerbating the demand for healthcare providers.
Telemedicine and mobile health solutions have become promising tools for closing the gap in healthcare access by using digital platforms to connect patients in remote areas with medical professionals. They are revolutionising the way healthcare services are provided in rural India. Through telemedicine, digital tools connect patients with doctors remotely, while mobile health services ensure that quality healthcare services reach the remotest corner on the wheels. This eliminates the need for in-person travel and allows for prompt medical intervention.
With the COVID-19 pandemic, the need for telemedicine and mobile health solutions has spiked, with government and private initiatives expanding access to primary care to rural areas where nearly 70 per cent of the population lives.
Telemedicine: A promising tool for rural healthcare
More than a tool for providing patient care, telemedicine provides solutions for bridging the primary healthcare gap in rural India. It enables important healthcare treatments to reach even the most remote places, where traditional healthcare infrastructure is frequently inadequate.
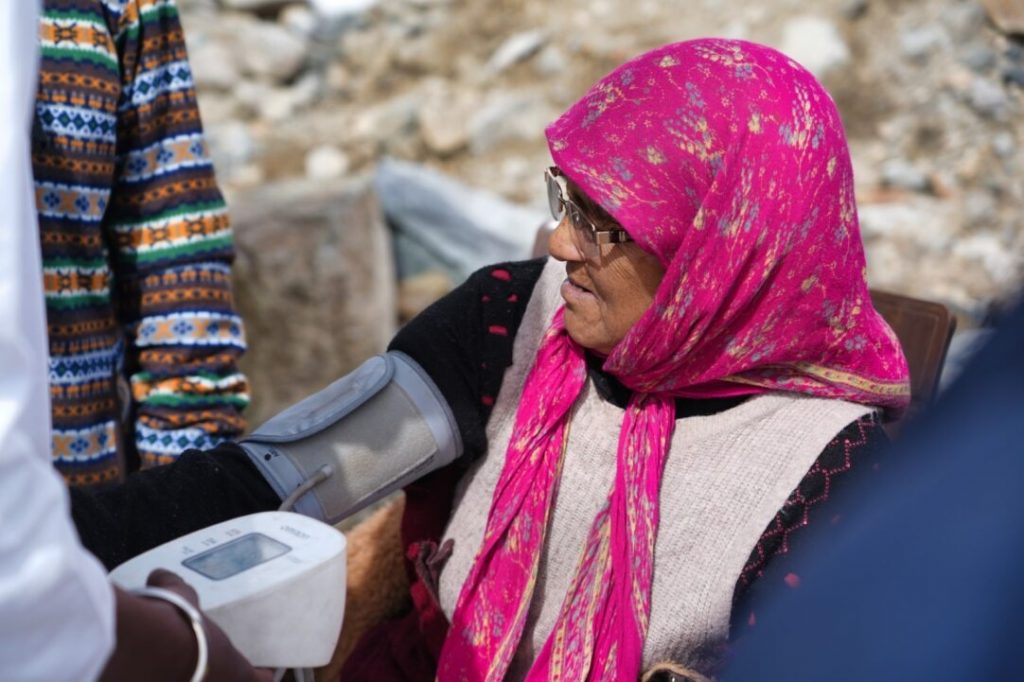
Telemedicine can transform the rural healthcare system and help solve transport issues, which are one of the primary causes of a lack of appropriate healthcare in rural areas. Telemedicine contributes to the region’s economic stability by reducing conveyance charges. Technology and advanced communication equipment promise to significantly improve the diagnosis and treatment of critical and chronic diseases. Further, since there is no need for physical appearance inside a clinic, telemedicine reduces waiting time, which increases doctor-patient interaction and consultation frequency. Other benefits include the immediate reviewing of test reports and imaging data by radiologists and doctors, which increases the likelihood of receiving prompt medical care. This includes a patient’s vital metrics, such as blood pressure, sugar levels, and blood oxygen levels, which can be monitored at regular intervals from the comfort of his home and recorded in the patient’s electronic files for prompt consideration.
When the rural population uses more technology and is aware of its benefits, access to quality healthcare worldwide grows exponentially, as do the options for receiving second and third opinions.
MMU: Delivering last-mile healthcare
On the other hand, Mobile medical units (MMUs) are specialised vehicles equipped with medical facilities and staffed by healthcare professionals designed to deliver essential medical services directly to underserved rural populations. Since their introduction, MMUs have been a revelation to the public. They have provided a definitive solution to many issues about whether high-quality healthcare can be made available directly to persons living in remote areas deprived of quality health services during an emergency. MMUs provide medical centre services to communities with limited access to healthcare. These clinics can take the form of buses, vans, or trailers that operate independently or as extensions of established healthcare organisations.
They enhance accessibility by reaching remote areas lacking adequate healthcare infrastructure addressing geographical, financial, cultural, and psychological barriers to care. MMUs offer cost-effective solutions by reducing the need for emergency hospital visits and associated expenses, as evidenced by cost savings observed in similar models globally. These units, equipped with advanced technology, including electronic health records and telemedicine capabilities, facilitate comprehensive care encompassing primary, preventive, emergency, and speciality services. By bringing healthcare services directly to patients, MMUs are crucial in improving health outcomes and bridging the healthcare gap in rural communities.
The gaps in between
However, several impediments prevent individuals from adopting telemedicine or expanding the services of MMUs. Limited smartphone access and dependable internet connectivity are major challenges, particularly in remote and rural communities. Many patients in these places may not have the necessary technology or expertise with telemedicine. Socio-cultural considerations also play a role, as many patients prefer face-to-face consultations and rely on traditional healthcare techniques. Privacy concerns, particularly in shared living circumstances, deter patients from properly utilising telehealth and MMU services.
Smile’s promise to accessible rural healthcare
With a population of over 1.4 billion, last-mile healthcare delivery in our country remains a significant concern. More than 65% of the population lives in rural areas with a lesser share of overall healthcare infrastructure, and urban slum dwellers emphasise daily survival over healthcare. Unequal distribution and a lack of information also hinder utilising available healthcare services. Addressing these gaps is critical to meeting Universal Health Coverage goals and supporting the Government of India’s aim of Ayushman Bharat.
Smile Foundation’s Smile on Wheels (SoW) initiative attempts to reach rural communities through professional healthcare services. These mobile Vans operate nationwide, treating approximately thousands of patients every year. It provided free medicines to individuals. A national-level multi-centric project, the project offers a comprehensive spectrum of healthcare services to poor people in remote rural areas and slums via an equipped mobile medical van. The program aims to provide the impoverished with various rudimentary, preventative, and curative health treatments.
Furthermore, the Smile Foundation focuses on improving telemedicine access by establishing telemedicine clinics in Primary Health Centres (PHCs) to boost primary healthcare access and minimise the burden at the primary healthcare level, utilising the public-private partnership model.