STEM education – short for Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics – played an all-important role in India’s IT revolution. The world-class IT industry spawned as a result led to sweeping economic and political transformations.
India’s tryst with the IT revolution shows that STEM education is essential for a developing nation. STEM skills can help address complex challenges of sustainable development—climate change, energy sufficiency, healthcare delivery, food security etc. Moreover, high STEM literacy enables nations to create new technologies and industries. This helps reduce dependence on imports and promotes self-sufficiency. A STEM-literate workforce also attracts foreign investment and fosters global partnerships and competition, resulting in job creation and economic prosperity.
It’s not hard to imagine then that a focus on STEM education will be key in transforming India’s future.
Advantages of focusing on STEM education
STEM education comes with advantages that last for years beyond the actual duration of the education. It develops a spirit of innovation through practical, interdisciplinary approach to problem solving. It further equips students with logical reasoning and critical thinking skills. These are core abilities that help in actively analysing, evaluating and applying knowledge towards tackling complex challenges. Thus, STEM education can prepare students for fulfilling careers that make full use of their cognitive abilities.
STEM fields are emerging as a popular choice among students. STEM skills feature heavily among the demands of tomorrow’s workforce. There is a high demand for software developers, data scientists, biotechnologists, medical researchers etc. In addition, demand for experts in fields such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain development, and quantum computing is growing. These fields are poised to transform the world as we know it.
So, how can we accelerate the STEM education revolution in India? To understand the way forward, we must first understand the current situation of education in India.
The current landscape of Indian education
Rote learning, exam-oriented curriculum and insufficient infrastructure and resources define India’s current education system, especially in the rural areas of India. An excessive focus on marks leads to a stifling of skills such as creativity, innovation, critical thinking, problem-solving and collaboration. As a result, the next generation of students is likely to be academically accomplished, but acutely unemployable. Application-oriented education is the need of the hour so that students can apply their STEM skills to real-life problems.
A huge digital divide between urban and rural sectors also marks India’s STEM education landscape. Rural India lags significantly behind in adopting digital technologies, and also lacks technological infrastructure and modern learning systems. A comprehensive Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)—including connectivity, devices, software, e-platforms and data centres—in rural centres can bridge this divide.
But there is cause for optimism, too. The Indian government and industry have undertaken various initiatives to address these challenges and boost STEM education in India.
Initiatives to foster STEM education in India
National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 – India’s first education policy of the 21st century, proposes the revamping of the current education structure. NEP 2020 places a particular emphasis on the transformation of STEM education in India.
Here’s how NEP 2020 aims to promote STEM education in India:
- The revised pedagogy in NEP 2020 aims to be more holistic, integrated, inquiry-driven, discovery-oriented, learner-centred, flexible and enjoyable.
- Education will emphasise the understanding of key concepts, ideas, applications and problem-solving abilities.
- Experiential learning and hands-on learning will take the focus away from rote learning.
- Coding will be introduced from class 6 onwards, giving students a head start in the competitive job market.
- School curricula will introduce key concepts in artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain programming etc.
- Students as young as 6-years old will learn foundational concepts in maths, computational thinking, machine learning, and data science.
- Multidisciplinary education that integrates humanities and arts subjects will break down silos and hierarchies in education.
Skill India and Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) – launched by NITI Aayog in 2016 – are also bringing STEM skills to the youth. As a part of the AIM, the government launched over 10,000 Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs) across India. More than 60% of these are in government and rural schools, widening access to rural areas. About 96% of the ATLs serve co-educational or all-girls schools, promoting gender equality. The EdTech industry, too, is bringing STEM labs, tinkering labs, 3D printing, electronics, IoT and sensors to Indian classrooms.
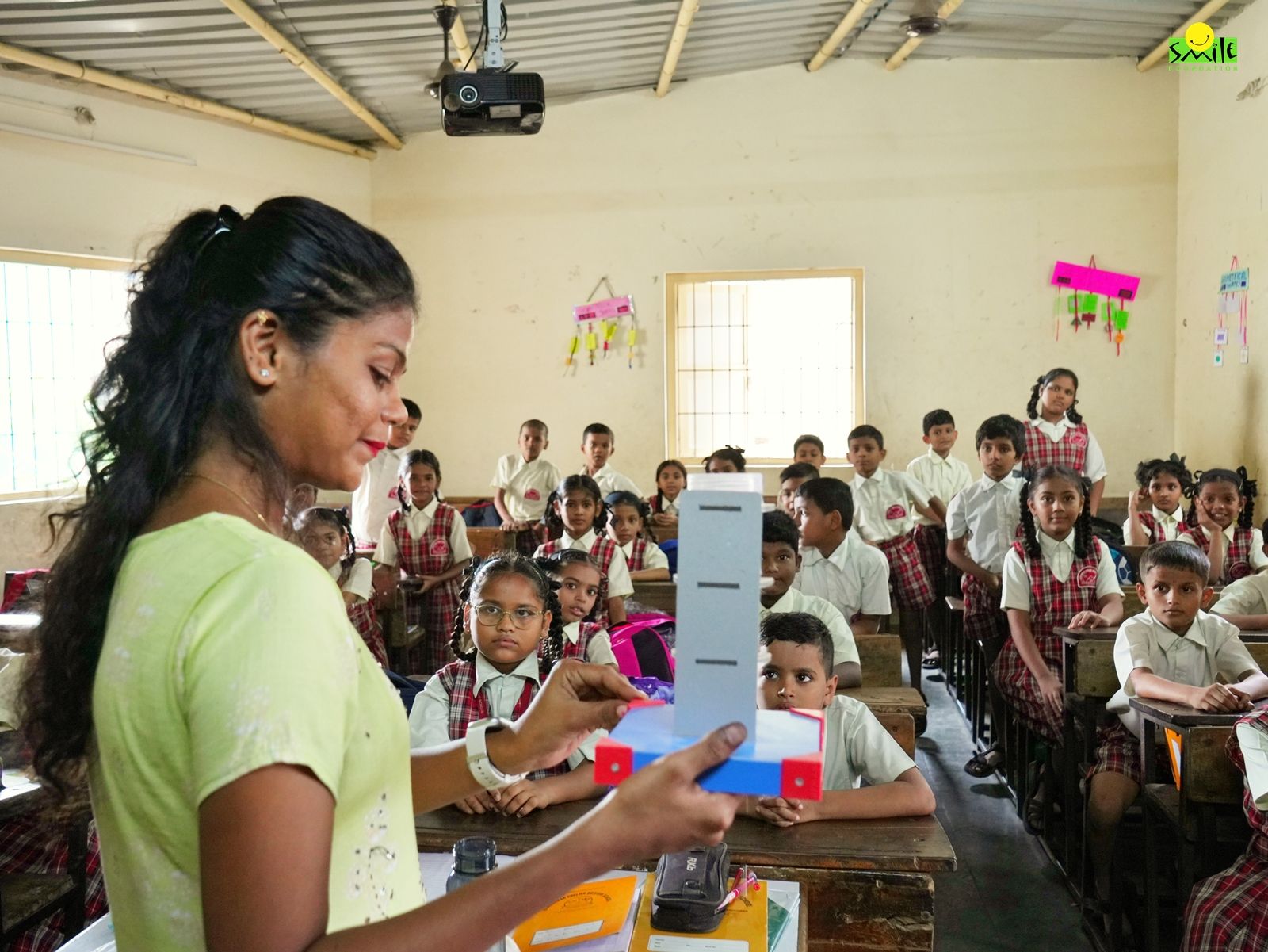
STEM education by Smile Foundation
Smile Foundation is spreading STEM education to the remotest parts of India. It conducts hands-on workshops and interactive sessions to empower educators with skills and innovative learning methods. To further integrate STEM education in schools, it also encourages project-based learning through aeromodelling, 3D printing, robotics, astronomy etc.
Smile Foundation recently joined hands with IIT Bombay to bring STEM education to young children. So far, 960 children have benefitted from this collaboration. Its NXplorers Carnival also empowered young minds in Andhra Pradesh to become future-ready with STEM skills.
Through its STEM initiatives, Smile Foundation is playing a part in nurturing the next generation of innovators, inventors and leaders. It’s only through such collaborations between government, schools, industry, and developmental organisations that India’s STEM revolution will take wings.
Your organisation too can become a flag bearer of innovation by partnering with us for STEM education of children here.