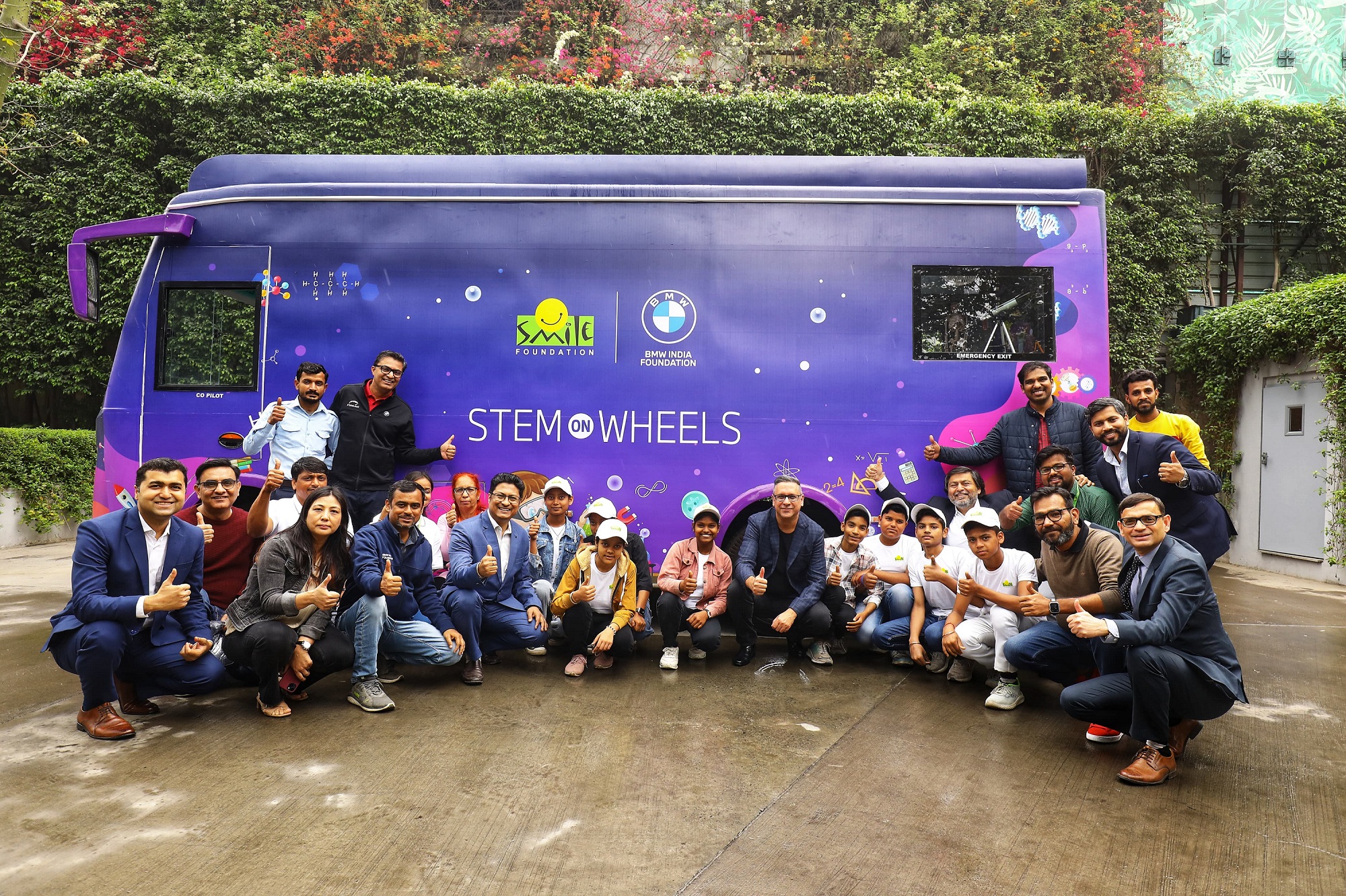
Last December, the Centre for Child Rights and Development (CCRD), Chennai, conducted a two-day training session for rural children in Chengalpattu district. “We wanted to talk to children about the safe use of technology for educational purposes. We discovered that they are mainly interested in using the internet to access social media,” says Stegana Jency, director, adding that girls were mostly accessing content on cosmetics and beauty while boys were searching for information on physical fitness and bodybuilding.
“We then asked them why they were not using technology to enhance their knowledge or skills or to supplement the school curriculum, especially as many of them find it difficult to understand certain concepts,” says Jency, adding that they also spoke to the children of using technology, and the internet, in a safe manner. “We made them realise the importance of using technology for learning. After the training, many have started accessing self-development websites and using the internet for their studies and to work on projects. But one session isn’t enough, we will need many more to help children in underserved areas use technology for educational purposes.’
Digital classrooms, e-learning platforms can help students, teachers
Technology can help bridge the education gap in underserved communities by providing equitable access to learning resources, and improving educational outcomes.
Or one, it provides access to educational content. Students in underserved areas can access free or low-cost educational materials, such as videos, textbooks, tutorials, and even courses through digital platforms. There are websites like Khan Academy, Coursera, etc that offer a vast range of subjects, allowing students to learn at their own pace. Free or affordable e-books and resources that are available online help students access learning materials without the financial burden of having to purchase expensive textbooks.
With access to technology and proper tools, students in rural or isolated locations can receive an education comparable to that of urban areas through video conferencing or digital classrooms. Online platforms allow students to connect with teachers and educational content in areas where schools lack proper infrastructure.
Technology can also help teachers in underserved communities improve their skills by offering them access to online professional development courses, webinars, and teaching resources. Digital tools like adaptive learning platforms can provide personalised learning by tailoring educational content to each student’s pace and learning style. This is especially useful in underserved communities where students may come from different educational backgrounds or have varying access to prior learning experiences.
Educational apps and online resources provide students with access to a wealth of information beyond textbooks. And schools are adopting new technology to improve learning.
A 2023 survey by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) revealed that over 65% of Indian schools had integrated some form of digital technology into their classrooms. This trend is only expected to increase in the coming years.
Technology can improve education in underserved areas
The Covid-19 pandemic highlighted the digital divide that exists between rural and urban areas. “Children in urban areas had the opportunities and space to access technology but it was a challenge in rural areas.”, says Stegana Jency, Director of Centre for Child Rights and Development (CCRD) in Chennai.
Technology can help bridge this gap. For example, eVidyaloka was founded with the vision of transforming rural education in India by leveraging technology and volunteer-driven teaching. Their programme primarily focuses on subjects such as Mathematics, Science, English, Digital Literacy, and Artificial Intelligence for students in grades five to 10, aligning with state education board curricula.
Technology is a game-changer in rural education. It eliminates geographical barriers, making quality learning accessible to students who would otherwise lack it. Through digital classrooms, organisations enable students in the remotest villages to learn from experienced teachers worldwide. Additionally- digital content, and interactive platforms enhance engagement and help students grasp concepts more effectively. With digital initiatives, all engaged stakeholders are preparing rural students to be future ready.
Government initiatives work to bridge the gap
The Indian government has launched several initiatives to leverage technology in rural education, such as ‘Digital India’. A flagship programme of the Government of India, it aims to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy.
PM e-VIDYA aims to unify all efforts related to digital/online/on-air education to enable multi-mode access to education. This will benefit nearly 25 crore school going children across the country.
Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA), an initiative of NCERT, is a national platform for school education. It can be operated through a web portal or mobile app and includes e-content corresponding to the curriculum meant for learners and teachers. According to the official website, it currently supports 108 languages: 101 Indian languages and 7 foreign languages.
There is also SWAYAM PRABHA, a group of 40 DTH channels devoted to telecasting of high-quality educational programmes on 24X7 basis using the GSAT-15 satellite. Every day, there will be new content for at least four hours, which will be repeated five more times in a day, allowing students to choose the time of their convenience. The content is provided by IITs, UGC, CEC, and IGNOU.
Other government initiatives include E-Pathshala, a website and app that provides access to educational resources like textbooks, audio, video, and periodicals. It was developed by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) in collaboration with the Ministry of Education (MoE).
And schools have been making an effort to integrate technology into their classrooms as it benefits learners and teachers. A study by the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) found that 92% of teachers believe that technology has made them more effective in the classroom.
Roadblocks that need to be overcome
Despite its transformative potential, digital education in rural areas faces several challenges. Limited internet connectivity, lack of access to digital devices, and infrastructural constraints can hinder the effectiveness of online learning. Additionally, digital literacy among students, teachers, and even parents needed to be strengthened.
It has been observed that girls in rural areas are impacted more. Very often, children who live in remote areas have to travel 10km or more to reach the town, where they can access the internet. Boys will go with other boys by bike and go wherever needed to access the internet but, when it comes to girls it’s more difficult as there are concerns about safety.
Many women and girls are not allowed to have their own mobile phones. Gender issues play a very important role in accessing technology.
Lack of knowledge of current applications is another hurdle. Though there are many websites and apps available that can be used to enhance reading and writing skills and also assist with the academic curriculum, few people are aware of it or how to use it. Even many teachers in underserved areas are not very tech-savvy. Sometimes the common understanding that emerges from the current classrooms is something like this- 21st century children are being taught by 19th century teachers in 18th century classrooms.
Often, parents, teachers and school management are also hesitant to allow children access to technology as they feel children will get “spoiled”.
Since many adults are not knowledgeable about the latest advances in technology, they are unable to guide children or teach them positive aspects of technology and how to use it safely so they simply deny them access to it. When an organisation conducted a training session on digital usage, out of 30 children, only one boy was aware of the risks involved in using mobile apps, social media, etc.
To address these issues, a multi-stakeholder approach is necessary—government support for ensuring smooth implementation, local partners for socio-economic context, corporate partnerships for funding/ support and community engagement to create awareness and ownership of learning.
NGOs help spread awareness
Smile Foundation is working to address the issue and leverage use of technology in education to help students in underserved areas.
Our educational initiatives have worked to improve our centres’ infrastructure through green infrastructure and digital classrooms including solar panels, smart class installation, learning software and educational tablets.
The Foundation also operates various scholarship projects in collaboration with esteemed donors like Deutsche Bank, Quantiphi, Quest Global, Siemens, and more. These projects collectively benefit thousands of students. Each scholarship recipient is provided with a laptop and other essential resources, ensuring that they have the technology required for online learning and research.
Under Mission Education, our flagship programme, we are setting up Tab Labs in schools in rural areas for young children. These tabs have video resources, reading resources, quizzes, a kids-friendly interface, and curriculum-mapped content as per their academic classes. We are committed to leaving no child behind in our efforts towards making Indian children ready for a developed India.