Bringing healthcare to rural India has been a longstanding challenge dating back to the British colonial era. Historical records reveal accounts of doctors being coerced into serving in rural government hospitals due to the lack of opportunities for private practice in rural areas. The inadequate facilities in Primary Healthcare Centres (PHCs) further deterred doctors from practicing in rural India, a challenge that persists to this day.
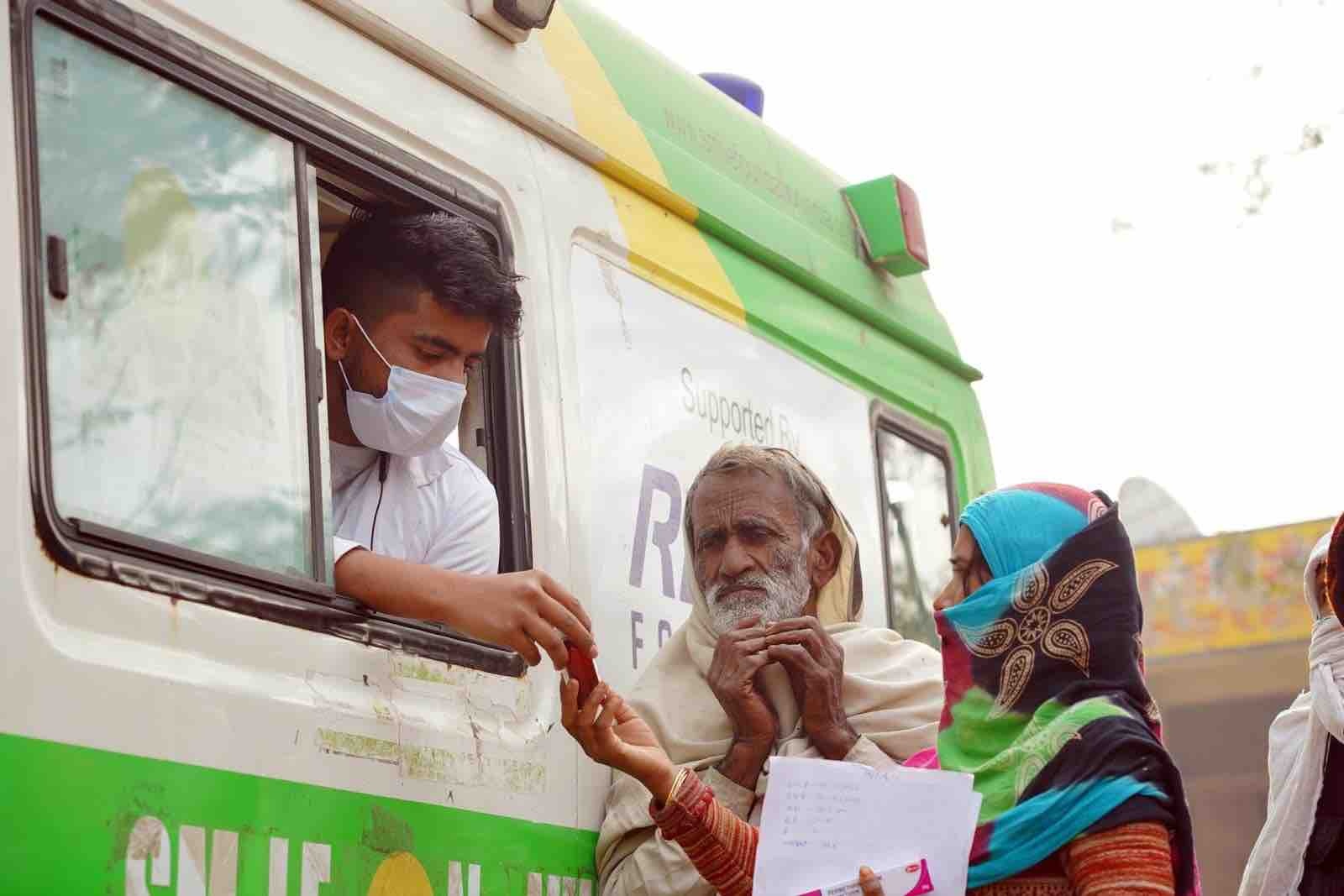
The dearth of doctors willing to work and reside in villages is just one obstacle hindering access to healthcare in rural India. In 58 current projects covered by Smile Foundation, which spans more than 700 villages and slums in 17 states of India, mobile medical units facilities are intended to serve a population of 10,00,000+ children and their families.
What about PHCs?
Doctors allocate only a few hours each day to see patients, and the majority of the PHCs are difficult to reach via public transport, exacerbating the challenge of access for vulnerable groups such as pregnant women, persons with disabilities, and the elderly.
The lack of reliable and regular healthcare access not only complicates the management of illnesses and emergencies but also contributes to a lack of awareness about practices essential for community health. Local residents often need to undertake long journeys to access medical treatment for common ailments. Moreover, due to limited access, individuals tend to ignore symptoms and delay seeking medical assistance until their conditions deteriorate, resulting in the treatment of many illnesses at advanced stages where complications have already arisen.
In cases of medical emergencies, ambulance services from distant hospitals are dispatched, often taking over an hour to arrive, if available at all. Consequently, many opt to hire private vehicles to transport patients to better-equipped hospitals, despite the considerable distance.
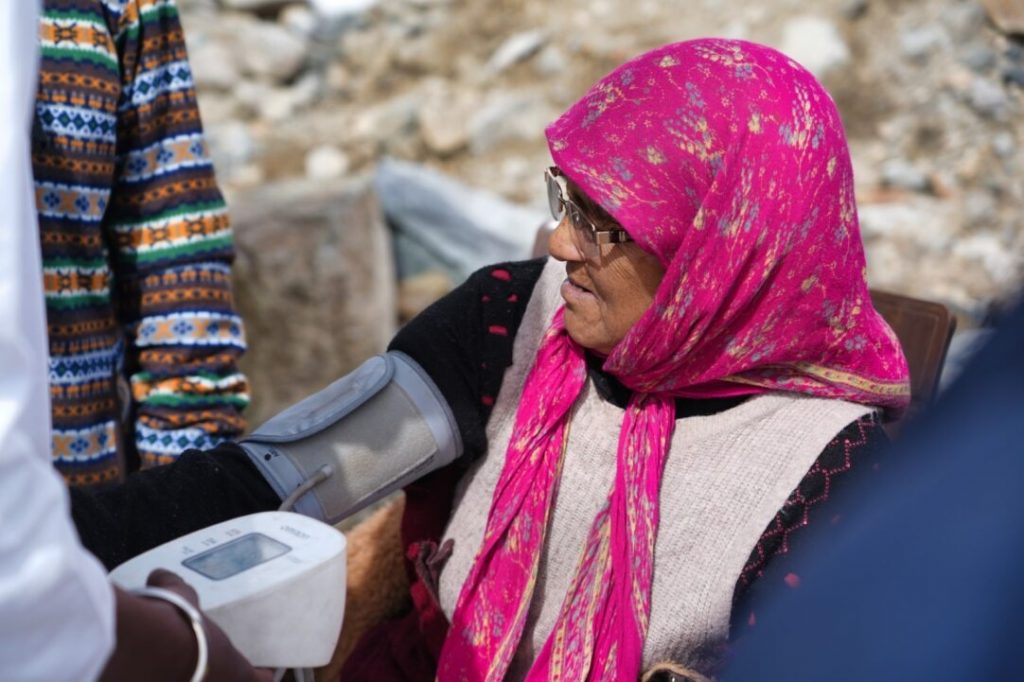
While the challenges of healthcare access during times of illness are significant, there is also a widespread lack of awareness regarding health and healthy lifestyle practices. PHCs attempt to address this issue by organizing weekly camps for pregnant women to provide guidance on maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle during pregnancy. However, due to the inaccessibility of PHCs, these camps are not as effective as desired.
Additionally, the need for dietary intervention extends beyond pregnant women to encompass individuals with conditions such as high blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes, which are prevalent in the project area. Despite doctors’ prescriptions, there is limited follow-up on recommended dietary and lifestyle changes due to the inaccessibility of most settlements.
When did the mobile medical units start?
The issues of healthcare access and awareness are not unique to India and have prompted various interventions over time. Mobile Medical Units (MMUs) have emerged as a solution to address these challenges by delivering healthcare services directly to rural communities. Initially developed for military use during World War II, MMUs gained popularity in civilian settings, including India.
One notable MMU initiative was the “Skippo” project undertaken by the All-India Women’s Conference (AIWC) in the aftermath of World War II. Initiated by sculptor Mrs. Hilda Seligman, the project aimed to improve healthcare access for rural Indian women by funding the operation of mobile health vans. The success of the Skippo project demonstrated the potential of MMUs to bridge the gap in healthcare access in rural areas.
In recent times, initiatives like Smile Foundation‘s MMUs have continued the legacy of providing healthcare to underserved rural populations. Funded by many corporates, MMUs operates in hundreds of settlements, staffed by a team comprising doctors, nurses, health workers, and drivers. The MMU visits each village in the project areas regularly, providing medical assistance, diagnosis, and health education.
The MMU team conducts consultations, provides treatment, and emphasises preventive measures to maintain overall health. Despite challenges such as limited resources and infrastructural constraints, the MMU played a crucial role in improving healthcare access and awareness in the rural areas it served.
Never undermining the importance of MMUs
In conclusion, initiatives like MMUs of Smile Foundation play a vital role in addressing the healthcare challenges faced by rural communities in India. By bringing medical services directly to the doorstep of underserved populations, MMUs contribute to improving healthcare access, promoting preventive care, and enhancing overall community health. However, sustained efforts and investment are needed to scale up such interventions and ensure equitable access to healthcare for all rural residents.