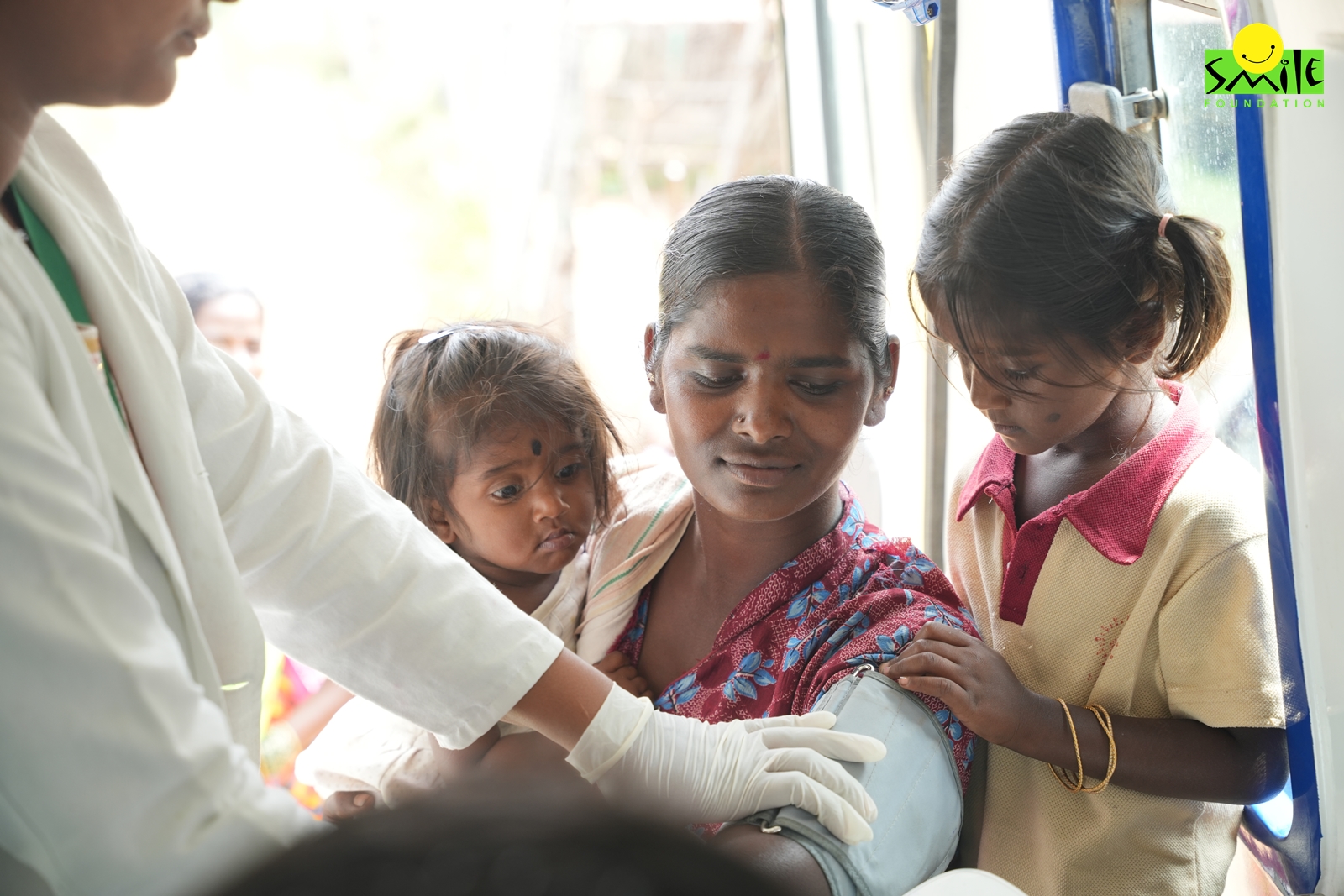
As women are now actively working as leaders and outperforming others in many areas of life, women’s empowerment in India is no more just a dream. The woman governors and the governments led by these extraordinary people are taking up the burden and pressing on in the struggle alone wherever necessary.
In India, a number of factors, including the geographical context (urban/rural), social position (caste and class), educational level, and age factor, all play a significant role in determining how empowered women are. There are initiatives to empower women at the state, local (panchayat), and federal levels.
However, women face discrimination in the majority of industries, including politics, economic involvement, health and medical care, and education. This shows that there are significant gaps between strategic developments and actual implementation on the ground.
The creation and execution of a clear policy framework, the promotion of civic consciousness, and education about women’s empowerment can help to achieve the goals of ending the struggle of women in Indian society. It’s also important to guarantee that they are accepted as legitimate equal co-workers.
Women Empowerment in India: A Background
The phrase “women empowerment” refers to leadership, or the power invested in women who share equivalent rights. The phrase describes the release of women from socioeconomic dependence.
Most of the women in the nation—roughly 50% of the total population—remain economically reliant on others. Most financially independent women exercise their free will, and live the lives they want.
But there is a sizable segment of women in our country that need upbeat encouragement. Many women are still not allowed to receive a basic education in the majority of Indian rural and semi-urban areas, despite having acquired the necessary knowledge.
The wonderful thing about women is that they excel in every area. However, in various parts of the world, they have been ignored. In turn, women endure inequality, financial dependency, oppression, and many societal ills.
The rights that males have are not similarly accorded to women in many places. Women are still expected to cook, clean, and receive lower pay. Women are held to high cultural and familial standards. Some Indian women let their husbands or parents make decisions for them.
Gender Inequality and the Reasons behind it
The belief that women are weaker is a strong reason to forbid women from working or studying far from their homes. In addition, some Indian women were compelled by their parents to be married at an early age. In today’s civilizations, women’s empowerment is absolutely necessary. It is crucial for both societies and the self-esteem of women.
Giving women the right is empowering them. Women can engage equally in politics, the economy, society, and education. As with males, women can pursue higher education. They can pursue a high degree of education, complete their coursework, pick any subject to study, and any skill to master.
By assuring them they can accomplish anything they set their minds to, women are encouraged to feel strong. Women have the option to make decisions and can work outside the house. Women don’t rely on males for anything. By working to the best of their skills, they can provide for their families.
Today, women can hold high-level positions just like males. Some women are elevated to high-level roles such as presidents, leaders, community heads, and others. Additionally, a large number of women are now active in politics, academia, and the economy.
Smile Foundation & Women Empowerment
The Smile Foundation launched a dynamic and transformative initiative, Swabhiman, translating into “self-respect” in hindi, in 2005 to address women-specific issues using a straightforward yet efficient strategy. Through creative communal activities, the programme especially aims to realise both individual and collective self-esteem and inner strength for marginalised and socially excluded women and adolescent girls.
Under Swabhiman, the initiative for women’s empowerment, a customised approach known as the “4 S Model” was devised. The abbreviation “4 S Model” stands for four cutting-edge strategies: Supporting Education, Sustaining the Change in Communities, and Seeking Healthcare as a Behaviour.
You can also contribute to the education of girls for women empowerment.